Growing Plants Using Hydroponics
Hello gardeners, we are back with a new topic again and the topic is all about how to grow plants using hydroponics. Do you want to grow plants by using hydroponics? So, if you want to grow plants by using the hydroponics method then you need to follow this complete article to know about growing plants using hydroponics. In this article, we will also mention all the requirements for growing plants using hydroponics.
Introduction to Hydroponics
Hydroponics may be a type of horticulture and a subset of hydro culture that involves growing plants without soil, by using mineral nutrient solutions in an aqueous solvent. Terrestrial plants may grow with only their roots exposed to the nutritious liquid, or, additionally, the roots could also be physically supported by an inert medium like perlite, gravel, or other substrates. Despite inert media, roots can cause changes within the rhizosphere pH and root exudates can affect rhizosphere biology.
The nutrients utilized in hydroponic systems can come from many different sources, that includes (but not limited to) fish excrement, duck manure, purchased chemical fertilizers, or artificial nutrient solutions.
Plants were commonly grown hydroponically, on inert media that include tomatoes, peppers, cucumbers, strawberries, lettuces, cannabis, and even model plants like Arabidopsis thaliana.
A Step-By-Step Guide for Growing Plants Using Hydroponics
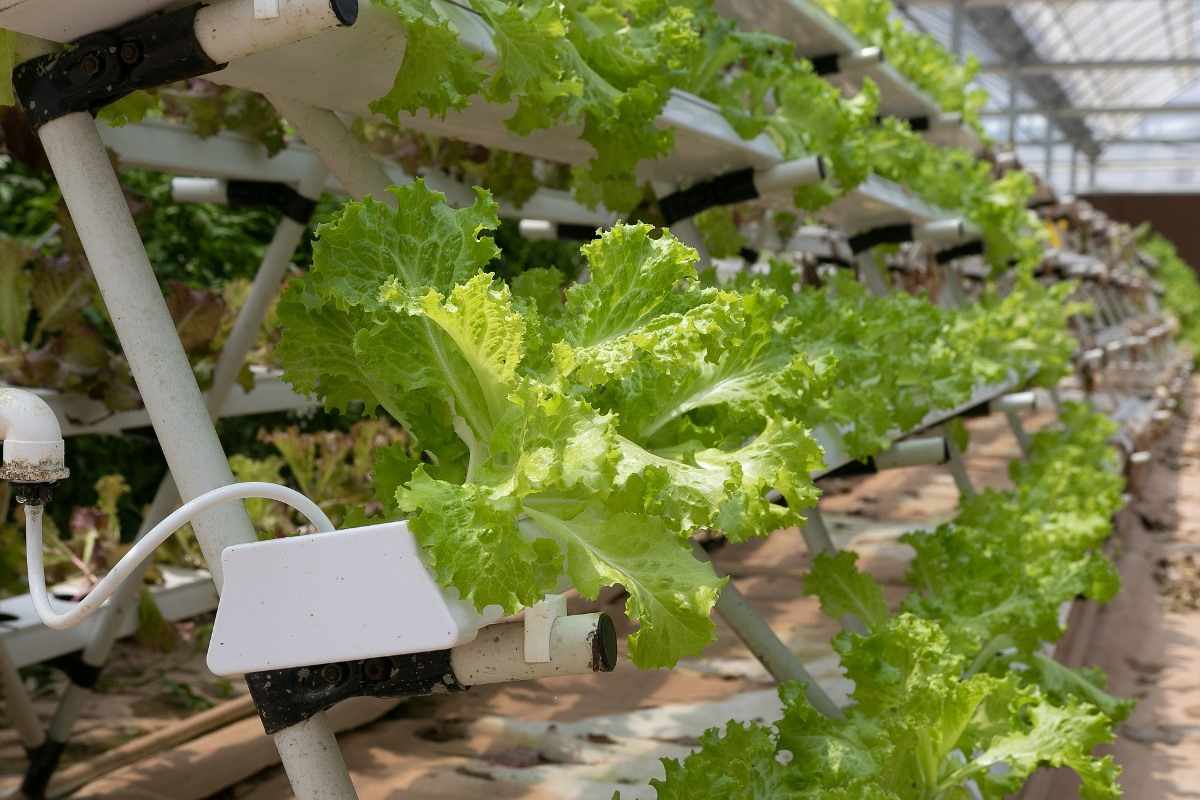

Have you ever dreamed to have a garden, but just don’t have the outdoor space? Hydroponic gardening is best for you. It is a very simple way to garden without using dirt and it can be done pretty much anywhere.
What Is Hydroponics?
Hydroponics may be a sort of gardening that uses no soil, but instead grows plants in a solution of water and nutrients. A hydroponic system can easily grow plants and vegetables faster than growing outdoors in soil and hydroponic systems are often used year-round. Plants grown hydroponically often yield more and they require very little space and use less water than with conventional gardening. A hydroponic system can also be a very good and perfect solution for apartment dwellers and urbanites that don’t have an outside gardening plot.
Four systems that are suitable for beginners getting started with are wick, water culture, and even ebb and flow. More advanced systems include the nutrient film technique and therefore the aeroponic system. The simplest plants to start with are greens like lettuce, spinach, Swiss chard, and kale; herbs like basil, parsley, oregano, cilantro, and mint; and fruiting plants like tomatoes, strawberries, and hot peppers.
Different Types of Hydroponics
When it comes to hydroponics systems, there are different six main types to choose from. These are listed below:
- Deep Water Culture (DWC)
- Ebb and Flow (Flood and Drain)
- Wicking
- Drip
- Aeroponic
- Nutrient Film Technique (NFT)
Water Culture System
A water culture, or lettuce raft, the system is another one that’s very easy to line up. The plants are placed in a Styrofoam platform that floats on top of the reservoir with the help of nutrient-enriched water. However, unlike with the wick system, you’ll get to aerate the water with a raft system. This technique is best for growing leaf lettuce, but only a few other plants grow well in this system. It’s not recommended for long-lived plants like tomatoes.
What you will need
- Equipment or tools
- Drill, rotary tool, or X-ACTO knife (optional)
- Grow light (optional)
- Air stone and pump
Materials
- Bucket or basin for water reservoir
- Water
- Hydroponic fertilizer (dry or liquid)
- Styrofoam sheet
- Seedlings in net pots
Instructions
- Set up the water reservoir
Fill the reservoir container with water and nutrients. The container should be opaque (not clear or translucent) and a minimum of 12 inches deep; an honest example maybe a 14-gallon Roughneck tote.
- Aerate the water
The most common and cheap aeration system is an air stone and pump. The air stone, an equivalent bubbler found in home aquariums, is placed within the water and connected to a vacuum pump outside the reservoir. The pump pushes the air through the stone, which blows out very tiny bubbles to distribute oxygen through the water.
- Set up your growing raft
Cut a floating Styrofoam platform to suit inside the highest of the reservoir. Cut holes to insert net pots. Net pots are usually plastic containers with perforated bottoms that contain a growing medium (coconut coir, perlite, clay balls) and seedlings. The roots will be got to be in touch with the reservoir water.
- Set up a light-weight fixture
If you’re using natural light, skip this step. Otherwise, found out a light-weight fixture above the growing tray. If using incandescent light bulbs, set them 24 inches from the plants. LED and fluorescent lights aren’t as hot; place those 6 and 12 inches, respectively, from the plants.
Ebb and Flow System
An ebb and flow system also called the flood and drain system, is slightly more complex in design but is extremely versatile. This technique works by flooding the growing medium with a water-nutrient solution, then it drains back to the reservoir.
What you will need
Equipment or tools
- Grow light (optional)
- Submersible pump
- Electronic timer
Materials
- Bucket or basin for water reservoir
- Two tubes (fill tube and drain tube)
- Water
- Hydroponic fertilizer (dry or liquid)
- Growing tray
- Stand for growing tray
- Seedlings in net pots
Instructions
- Set up the water reservoir
The reservoir needs to be placed directly below the flood tray’s stand with the water and nutrients. You’ll use equivalent water for a few weeks at a time, ensuring to renew the nutrients whenever you modify the water.
- Connect a fill tube and drain tube
Connect the reservoir to the tray via a fill tube and a drain tube. The fill tube attaches to a submersible pump with a timer, which will help to control the flow of water up into the flood tray. The drain tube allows gravity to tug the water heater into the reservoir after flooding so that the water is often reused.
- Connect a submersible pump and timer
A submersible pump with a timer allows for tons of control in this sort of system. You’ll customize the length and frequency of watering supported by your plant’s needs.
- Set up the flood tray
The plant tray or flood tray, may be a large and shallow container on a tall stand. Plant your seedlings in perforated pots crammed with a growing medium, like perlite. The pots that your seedlings are in should be about twice as deep because of the flood tray.
- Set up a light-weight fixture
If you’re using natural light, skip this step. Otherwise, found out a light-weight fixture above the growing tray. If using incandescent light bulbs, set them 24 inches from the plants. LED and fluorescent lights aren’t as hot; place those 6 and 12 inches, respectively, from the plants.
Wick System
The wick system is that the simplest mechanically, as there are not any moving parts or electrical components. This technique isn’t ideal for water-hungry plants like lettuce or tomatoes, as they’ll spend the nutrient solution faster than the wicks can supply it. This technique works best for micro greens, herbs, and peppers.
Instructions
- Set up a water reservoir
Create a reservoir crammed with water and nutrients. This reservoir sits beneath the tray just by holding your plant and even growing medium.
- Connect wicks to the growing tray
Connect one or two wicks through holes within the bottom of the growing tray. If you would like to form holes within the growing tray, use a drill or screwdriver. The wicks will take in water from the reservoir and draw it up the wicks to the growing medium within the tray.
- Set up a growing tray
The growing medium, containing a seedling, is about above the water reservoir. Use a medium that will not drain too fast and can utilize the capillarity of the wick most effectively, like vermiculite, perlite, and soilless mixes.
- Set up a light-weight fixture
If you’re using natural light, skip this step. Otherwise, found out a light-weight fixture above the growing tray. If using incandescent light bulbs, set them 24 inches from the plants. LED and fluorescent lights aren’t as hot; place those 6 and 12 inches, respectively, from the plants.
Aeroponic System
An aeroponic system may be a more complex hydroponic method. Plant roots are suspended within the air and misted every jiffy with a water and nutrient solution. It’s a highly effective method but one that needs sophisticated pumps and misters. If the equipment malfunctions, the plant roots can dry out and die very quickly.
What you will need
Equipment or tools
- Drill or rotary tool (optional)
- Grow light (optional)
- Air stone and pump
- One tube (spray tube)
- One submersible pump
- Sprayer/misting head
Materials
- Bucket or basin for water reservoir
- Water
- Hydroponic fertilizer (dry or liquid)
- Tube or PVC pipe to suit the seedlings
- Seedlings in net pots
Instructions
- Set up a water reservoir with aeration
A container crammed with nutrient-filled water is positioned under the growing chamber. Add an aeration bubbler to the reservoir to oxygenate the water. This reservoir will also act as a catch basin for misted droplets of solution.
- Connect a submersible pump
Connect a pump to a mister or sprayer. The reservoir solution pumps to the mister or sprayer via tubing from a submersible pump tube within the reservoir. The sprayer is going to be aimed toward the plant’s root in a growing chamber.
- Set up the growing chamber
Similar to the nutrition film technique, you’ll found out tubes or channels for evenly suspending each seedling’s roots.
- Set up a light-weight fixture
If you’re using natural light, skip this step. Otherwise, found out a light-weight fixture above the growing tray. If using incandescent light bulbs, set them 24 inches from the plants. LED and fluorescent lights aren’t as hot; place those 6 and 12 inches, respectively, from the plants.
Nutrient Film Technique (N.F.T)
The nutrient film technique uses a water-nutrient solution that constantly flows in a loop from a reservoir through a growing tray, where plant roots are suspended and absorb nutrients because the solution flows by. This technique makes the ebb and flow system a continuously flowing system, never taking periodic breaks. A nutrient film system works well and best with fast-growing, shallow-rooted plants like lettuce, spinach, radishes, and herbs.
What you will need
Equipment or tools
- Drill or rotary tool (optional)
- Grow light (optional)
- Air stone and pump
- Submersible pump
Materials
- Bucket or basin for water reservoir
- Water
- Two tubes (fill tube and drain tube)
- Hydroponic fertilizer (dry or liquid)
- Tube or any PVC pipe to suit the seedlings
- Seedlings in net pots
Instructions
- Set up the water reservoir and aeration
The reservoir is placed directly below the flood tray’s stand with the water and nutrients. You’ll add an aeration bubbler within the reservoir to oxygenate the water.
- Connect the fill tube, drain tube, and even pump
Connect the reservoir to the tray via a fill tube and a drain tube. The fill tube attaches to a submersible pump, which controls the flow of water up into the flood tray. The drain tube allows gravity to tug the water heater into the reservoir after flooding so that the water is often reused. Unlike the ebb and flow methods, you are doing not need a timer, since it’s continuously pumping the water.
- Set up the growing tray
Instead of a flat tray, this method uses tubes or channels for the grow tray. The tubing is often set at an angle to form sure that the nutrient solution flows onto the roots. You’ll use a round tube or PVC pipe with holes drilled to suit internet pots or seedlings.
- Set up a light-weight fixture
If you’re using natural light, skip this step. Otherwise, found out a light-weight fixture above the growing tray. If using incandescent light bulbs, set them 24 inches from the plants. LED and fluorescent lights aren’t as hot; place those 6 and 12 inches, respectively, from the plants.
Simple Steps for Growing Plants Using Hydroponics
How to Prepare?
- Do not go overboard buying hydroponics supplies that they will need within the future but will not need within the beginning stages of hydroponic gardening
To begin your hydroponic gardening project you’ll only need a couple of things to urge you off to an excellent start. Many of the things you would like for hydroponics can already be found around your house so you’ll economize before you go full tilt into this hobby or found all at once in a hydroponic garden.
- Create a fanatical area for his or her gardening
Most newbie gardeners can either purchase an easy-to-install grow room or they can build a greenhouse outside of their home. Small grow rooms for the start hydroponic gardeners are usually slightly larger than a closet and maybe completely installed in under an hour.
- Get the proper hydroponic supplies
A small greenhouse can cost considerably more because you’ll get to either include a cement floor and system or lay other sorts of flooring like gravel before you build the greenhouse itself.
The basic items you would like after you opt on either a grow room or greenhouse include a temperature control unit, fan, heating mats, lighting fixtures for your blue and even red spectrum lights, an aeration system that is an aquarium system that works well for little gardens, pearlite, marble, and Styrofoam work well as a beginning medium and Rockwool, oasis or Rapid Rooters. Typical beginning tables for your plants include plastic tubs, a child’s swimming bath, or an aquarium. A gardener also can buy any of the things they have for his or her grown room from stores specializing in hydroponic supplies.
How to Germinate Seeds?
- Choose the seed that you want to grow
You need to make sure that it can be grown where you live and that it isn’t a plant that is grown underground.
- Take a wet paper towel and then place the seeds inside them
Fold it over, and then place it gently in a clear, sealable bag.
- Put the bag in a very warm, dark place and give the seeds some time to germinate
Germination is triggered when a seed is wet, so you need to keep the paper towels moist. You should not forget that some seeds take longer than others.
How to Transfer Seedlings?
- Keep in mind that, when the seeds have germinated and are showing a minimum of one inch of stem, it’s a seedling
What you are doing next depends on the sort of plant.
If the seed features a frailer stem, keep it within the original towel but cut small holes for the leaves to emerge through.
If the seed features a stronger stem, be happy to hide only the roots in wet paper towels and let the stem straighten out and grow leaves.
- Watch the seedlings carefully so that they grow straight
This is a fragile time in their life, so be extremely gentle.
Caring Tips for Plants
Better to move your plant into its permanent container when the seedling is stronger and even bigger.
Then fill the container with water. You can easily choose between having one plant per container and doing a larger container with many plants. If you choose the second option, then make sure that all the plants have very good support.
You need to place your grown seedling into the water so that only the roots are submerged. If you are growing a plant that gets much taller, then you should probably tape support to the side of the container.
You need to change the water every few days, especially if it seems to get murky or translucent. Also, plants need nutrients to grow well, so better to buy a pack of liquid fertilizer to add to the water every week. Follow the package instructions, and do not over feed the plants.
How to Mature Plants?
- If you chose a plant that bears fruit, then watch for flower buds growing near the leaves.
They will open and dry up, by leaving behind the start of a fruit or vegetable.
If the plant needs cross-pollination to be fertilized, then place the plant outside or near an open window for a few days so that insects can do the job easily. A very good plant for hydroponic gardening is one that self-pollinates.
- Make sure that the flowers do not weigh the stem down if you chose a good flowering plant.
Normally, plants can easily anchor themselves into the dirt for extra support. So, check your plant’s stem daily for any cracks or bending points.
- Harvest the fruit or vegetables like any other plant and then enjoy your hydroponic garden.
Hydroponic Growing Tips
In case if you miss this: How To Grow Strawberries In Greenhouse.

- Most edible plants require a minimum of six hours of sunlight each day; 12 to 16 hours is best. Confirm to place your lighting system on a timer, therefore the lights activate and off at an equivalent time every day.
- The good and best lighting for a hydroponics system is high-intensity discharge lighting fixtures, which may include either high-pressure sodium or metal halide bulbs. Halide bulbs emit a more orange-red light, which is great for plants within the vegetative growth stage. T5 is another sort of lighting utilized in hydroponic grow rooms. It produces a very high-output fluorescent light with low heat and low energy consumption. It’s ideal for growing plant cuttings and plants with short growth cycles.
- Ideal temperatures are between 20°C and 21°C. High temperatures may cause plants to become stunted, and if the water temperature gets too high, it’s going to cause plant disease.
- The ideal humidity for a hydroponic grows room is from a 40 to 60% ratio. Higher humidity levels—especially in rooms with poor air circulation—can cause mildew and other fungal problems. Consider a humidifier or dehumidifier to regulate the ratio.
- Your grow room should even have an ample supply of carbon dioxide; your plants will grow faster. The simplest thanks to getting CO2 to your plants is to form sure space features a constant flow of air. If necessary, invest in a fan or air circulation equipment to enhance the airflow.
- Hard water that contains a high mineral content won’t dissolve nutrients as effectively as water with lower mineral content, so you’ll get to filter your water if it’s high in minerals.
- The ideal pH level for water utilized in a hydroponic system is between 5.8 and 6.2 (slightly acidic). If your water doesn’t meet this level, chemicals are often wont to adjust the pH into the perfect range.
- The nutrients (or fertilizers) utilized in hydroponic systems are available in both liquid and dry forms, also as both organic and artificial. Use fertilizers that are designed for hydroponic gardening; don’t use standard fertilizers. The fertilizer should have the most macronutrients—nitrogen, potassium, phosphorus, calcium, and magnesium—as well as micronutrients iron, manganese, boron, zinc, copper, molybdenum, and chlorine.
- How to Grow Hibiscus from Flower
- Plantation Ideas for Home Decoration: A Beginners Guide
- Flower Garden Designs and Layouts for Beginners
- Planting and Spacing Techniques in Papaya: A Beginner’s Guide
- Growing Gold: Essential Techniques for Planting Pineapples
- How to Make Kalanchoe Plant Bushy: Home Remedies and Solutions
- 11 Reasons Why Your Gardenia is Not Blooming: Home Remedies and Solutions
- Eco Elegance: The Guide to Designing a Drought-Tolerant Landscape
- Gardening on a Slope: Strategies for Hillside Landscaping
- Nourish and Flourish: Top Organic Mulches for Thriving House Plants
- Everything You Want to Know about Indian Mogra Flower: Discover Uses and Growing
- Green Thumb Success: Expert Tips for Cultivating Greenhouse Pumpkins All Year Round
- Maximize Growth & Flavor: The Ultimate Guide to Companion Planting in Herb Gardens
- How to Control Rhododendron Problems Naturally: Home Remedies and Organic Ways to Fix Them
- Natural Magic: The Remarkable Benefits of Cinnamon for Plants
- Best Steps to Revive Dying Tulip with Natural and Organic Treatment
- 10 Reasons Why Your Angel Trumpet is Not Blooming: Remedies and Treatment
- How to Fix Periwinkle Leaf and Flower-Related Problems: Natural Remedies and Solutions
- How to Fix Zinnias Leaf and Flower Problems: Discover Natural and Home Remedies
- Organic Steps to Induce Lemon Tree Flowers: A Comprehensive Guide
- Bloom Booster: Crafting the Perfect Homemade Bougainvillea Fertilizer