Introduction: Hello gardeners, we are here with a great information of different types of vegetable garden layout designs. Vegetable gardening is the practice of growing and cultivating vegetable plants. Vegetable gardening is considered by lots of people to be a relaxing activity. Vegetable gardening is always an excellent and environment-friendly idea and if you can go for sustainable gardening then it will be even more helpful for all.
Growing vegetables in your home or garden are good for you, your neighborhood, and for helping to reduce carbon footprint. Growing vegetables can be done in a single pot on your patio or a larger scale depending upon space and time you have obtainable.
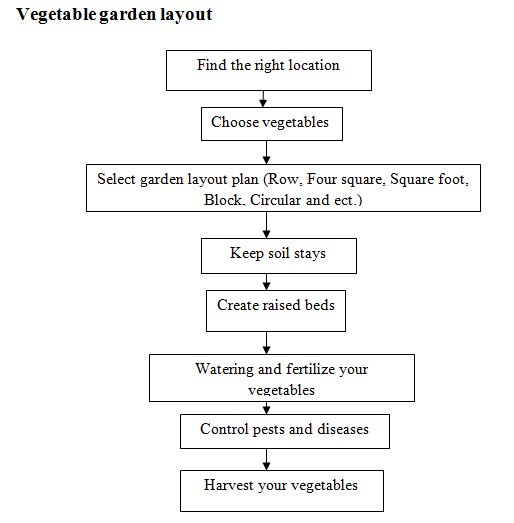
A step by step guide to Vegetable garden layout
Layout options for the vegetable garden before planting a vegetable garden layout, there are a few things to consider. The vegetable garden will thrive in well-draining, nutrient-rich soil. It’s probably a good idea to perform a soil test to verify its composition. Once the results are in, you will know if and with what the soil needs to be amended and you can add compost, sand, humus, fertilizer or other ingredients. The garden must also be located in an area of full sun. If there is no adequate area in the landscape, vegetables can be planted in containers on a deck or patio that receives the sun.

Here we discuss some of the most common garden layout plans for growing vegetables;
The rows type gardening layout
The most basic vegetable garden plan consists of design with straight, long rows running north to south orientation. North to south direction will ensure that the garden obtains the best sun exposure and air circulation. A garden that runs east to west tends to get too shaded from the vegetable crops grown in the preceding row.
Grow tall items such as corn or beans, on the north side of the garden to maintain them from shading smaller crops. Medium-sized plants like tomatoes, squash, and cabbage, must be grown in the center. Short crops like carrots, lettuce and radishes must grow in the southern end of the garden.
The four square gardening layout
Another vegetable garden layout idea is called a four-square garden layout plan. Imagine the bed divided into four quarters as if you have a piece of paper and draw a square on it and then across inside the square.
Heavy feeders like corn and leafy greens require lots of nutrients and will be included in one square bed. Middle feeders, for example, tomatoes and peppers, will be in another. Turnips and carrots are light feeders that like potash in the soil and will be developed together accordingly. Soil builders are those veggies that leach nitrogen into the soil, for example, peas, and will be grouped.
The square-foot gardening layout
Square-foot gardening (SFG) makes efficient use of space. Normally, an SFG garden is made of multiple 4 x 4-foot “boxes” or deeply-raised beds that can be densely planted for multiple harvests. A lattice is laid across the top to divide each square foot. SFG is an especially helpful process for beginner gardeners.
You should not miss the Vegetable Gardening Calendar.
The block gardening layout
Another garden layout plan is called the block type garden layout. It is also called close row or wide row planting; this process increases yields significantly over a traditional row style garden. It suppresses weeds. The idea is to plant vegetables in rectangular beds instead of long single rows, similar to that of the square foot but with whatever measurements you require. It will eliminate the need for surplus walkways, thus maximizing premium gardening space.
The circular vegetable garden layout
This plan is probably not the best for a newbie, but if you have been gardening for some time and have an excellent handle on it, you may want to try designing a circular vegetable garden. This can be quartered off to provide you specific sections, with the tallest plants growing in the middle and the shortest to the outside.
The backyard garden layout
A backyard garden often has many family demands placed upon it. It can be a place to relax and unwind a space for children and pets to play, and an area for growth as well as vegetables all at the same time. Backyard gardens can be grown in traditional in-ground rows raised bed garden beds or a mixture of both.
The vertical vegetable garden layout
Growing vegetable gardens vertically is yet another choice. These garden layouts are designed for people having little to no traditional garden space. Rather than planting in a typical garden bed, you take advantage of vertical space, growing plants along trellises, hanging baskets or even upside down.
The raised bed or containers garden layout
Again, for those having little space or even inadequate soil, planting vegetables in raised beds or containers is a great alternative. With this layout option, the sky is the limit, as you have the flexibility in moving the vegetable garden around and making use of all available space, including vertical areas.
The kitchen garden layout
Many fresh vegetables taste much better when they’re freshly harvested and what could be more convenient than having them just outside the back door. Kitchen gardens are planted and replanted throughout the season for a continuous supply of fresh vegetables for the kitchen.
The multiple bed layout plans
A multiple raised bed garden is designed to produce enough food to feed a large family year-round. The best part about this large garden layout is that you don’t have to worry as much about vegetable placement because most varieties won’t be planted in the same garden bed. This type of garden bed also allows you to add in some flowers around your vegetable patch. Furthermore, some vegetable varieties can help keep pests away while encouraging beneficial pollinators.
You may also consider reading the Growing Banana in Containers.
Some important tips for planning a vegetable garden layout;
- Whichever type of vegetable garden you choose, locate your vegetable garden in full sun.
- Train and trellis vine plants such as cucumber and squash to grow upwards to receive maximum production and save valuable vegetable gardening space.
- Carefully plan to use mulch, brick, or stepping stones to form paths to the plantings.
- Plant perennials or low growing shrubs as borders, preventing run-offs and some weeds.
- Avoid planting near big trees that will block the sunlight and take the water away from your vegetable garden.
Creating a vegetable garden plan
When creating a vegetable garden plan, there are several variables to consider
- The size of the garden the amount of sun your garden gets throughout the year,
- The length of your growing season,
- The number of people the vegetable garden will be feeding what you all like to eat,
- The space those plants take to grow what you would like to can, preserve or freeze the needs of the plants you want to grow the process of gardening you are using (raised beds, rows, Square Foot, biointensive, etc.) what was successful in the garden last season, and where you planted it.
Garden layout considerations

When deciding the best layout for a vegetable garden, there are a few things to take into consideration. They are;
Light
Almost all vegetables require at least 6 hours of full sun daily to do their best. Be sure that you think about this when selecting a site for a vegetable garden and watch the sun carefully during the day to be sure that the light is ample. Remember that the light angle and intensity changes with the growing seasons.
Water
Vegetables require plenty of water, particularly when they are establishing roots and during dry spells. Locate vegetable garden in an area that is near a water source such as a rain barrel, well tap, or water spicket. You may wish to consider installing an irrigation system if your layout is very large.
Function
When designing a vegetable garden, you need to allow not only enough space to grow particular vegetables but space to walk among the plants without compacting the soil. Create beds no more than four feet wide, and allow 2 to 4 feet in between the beds to accommodate your wheelbarrow and other equipment.
Different vegetable garden layout ideas
- You don’t have to follow one vegetable garden layout or another. You can simply combine the two by creating a vegetable garden that utilizes both raised beds and rows type garden. It all depends on specific needs and creativity.
- You can even get quite funky with the vegetable garden layout and make something unique.
- For those that live in apartments or condos, you may want to use strictly containers. Arrange similar vegetables together to create maintenance a bit easier. Group them in one or two areas, therefore, they can all be watered at the same time.
- Use hanging baskets and window boxes to increase the number of vegetables you can produce.
You may be interested in Beetroot Cultivation Income, Yield, Profit.
Excellent gardening information. Helps me find out what veggies are best to grow. thanks.